
#LEECH BLOOD MANUAL#
Manual restraint is possible in some species, but it carries a high risk of injuries and intense stress for sampled animals. However, blood sampling is a challenging clinical procedure in such conditions, with anesthesia needed in most cases. Veterinary health assessment of animals in zoological collections or in semi-wild and wild conditions requires collection of blood samples for variety of qualitative and quantitative analyses, such as hematological, biochemical, genetic and endocrinological profiling, or screening of pathogenes causing infectious diseases. This opens new opportunities for a significant improvement to animal welfare in zoological gardens, conservation programmes, and ecophysiological research, where quantification of blood parameters is often needed. Our data thus suggest that medicinal leeches can be used as a reliable non-invasive and stress-reducing alternative to standard venipuncture, even for quantitative assays. As the parameter alterations and correlations were similar among species, simple cross-species regression formulas were sufficient to correct the alterations, thereby ensuring good repeatability between leeches and venipuncture in most parameters. Although most hematological and biochemical parameters were significantly altered in leech-derived samples, their values showed strong ( r = 0.62–0.79 10/24 parameters) to very strong ( r > 0.8 13/24 parameters) correlations with venipuncture in all blood parameters, except for sodium ( r = 0.39). The leeches drew up to 20 ml of blood in 20 to 55 min. Medicinal leeches were manually applied on 67 zoo animals of eleven species, and control blood samples were obtained by venipuncture of the jugular vein. Hence, the aim of this study was to evaluate the suitability of the leech blood sampling method for quantification of hematological and biochemical parameters.
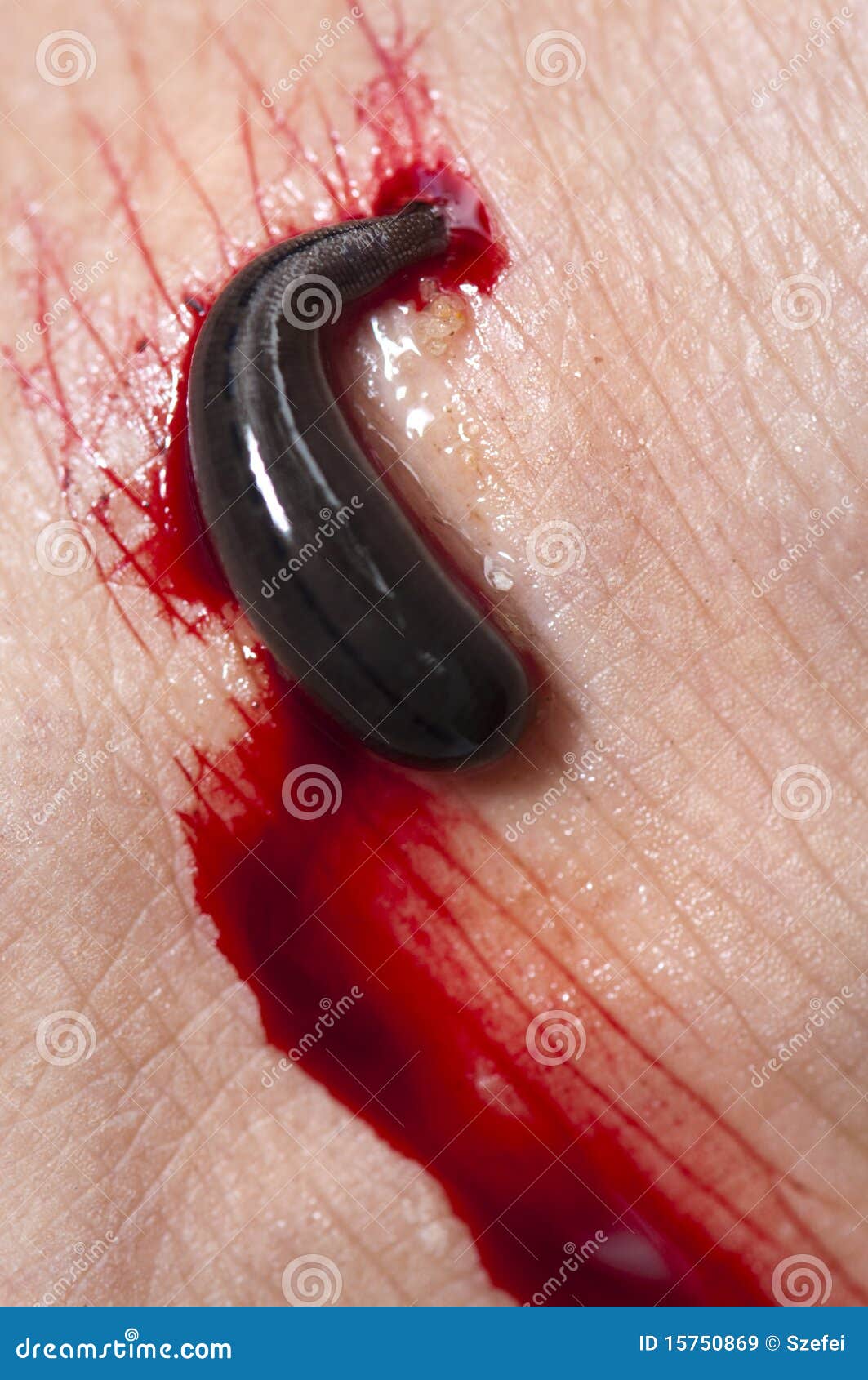
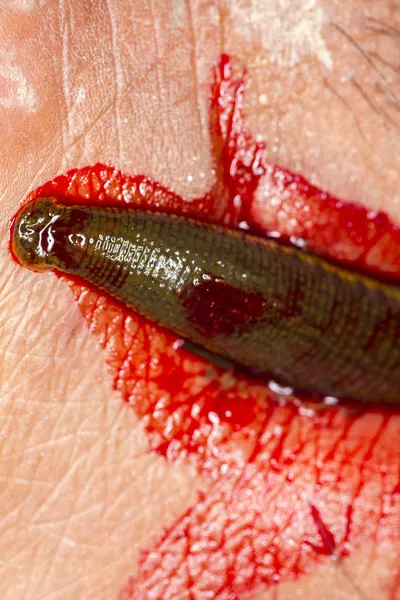

Blood sampling using medicinal leeches ( Hirudo medicinalis) represents a promising non-invasive alternative to venipuncture however, leech blood meal was to date used only for qualitative analyses such as genetic or serological screenings. Although manual restraint or anesthesia are usually possible, they entail intense stress and a high risk of injuries or organ failure.
#LEECH BLOOD PATCH#
It can't be stored in a Refrigerator, although patch notes 242.3 state it can, and there have been no contrary patch notes since.Pavel Kvapil 1,2 *, Oldřich Tomášek 3,4 *, Eva Bártová 2, Mojca Harej 1, Marjan Kastelic 1, Tit Primožič 1, Nikola Kašpárková 2 and Jožko Račnik 5.It can be stored in a Preserving Bin, but that doesn't extend its spoil time.It can be consumed but there has been no recorded effects or symptoms of disease after.It is also used as a bait when Fishing, as an alternative to using Sap or Giant Bee Honey.
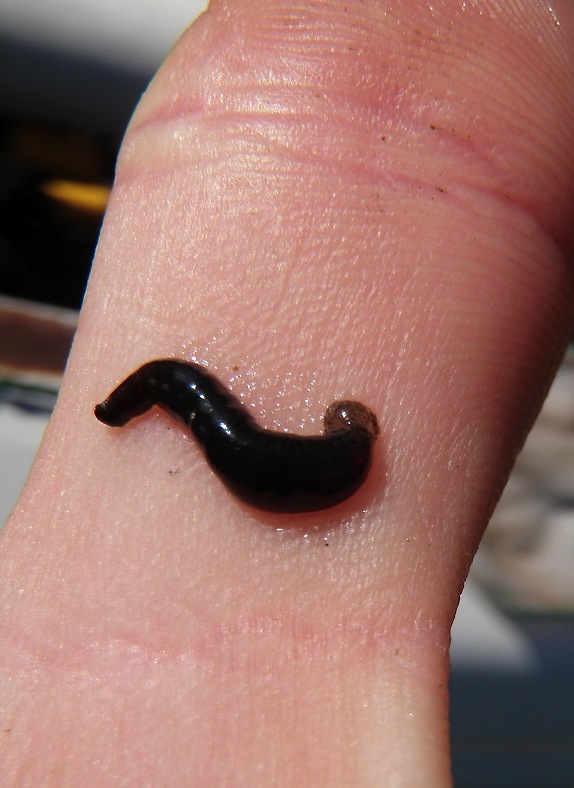

Items crafted with Leech Blood or Horns (Deathworm or Woolly Rhino): On Aberration, Leech Blood can be collected from lampreys found in the blue zone. A Rex or Spino is recommended for this reason. This method will work with any carnivore but to be safe from Kaprosuchus' grab ability make sure your Dino is immune to it, usually by being too big to carry. Using a Dino will prevent leeches from becoming attached to the player. Once finished, harvest them using the Rex or a Hatchet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
